Discover the Health Impacts of Masturbation
Unveiling the Truth Behind the Taboo
Published: December 19, 2023 (Updated: January 24, 2026)
We may make money when readers purchase items through our links. Disclosure

Masturbation has been stigmatized, shrouded in secrecy, and misunderstood due to societal norms and outdated taboos. But what if this ‘solo activity’ is the unsung hero in the realm of wellness, hiding a list of surprising health benefits under its veil? Let’s pull back the curtain and take an unbiased look at the health side of masturbation, dispelling myths and misconceptions along the way.
Navigating the complicated world of human health and wellness can be challenging, especially when it comes to topics still cloaked in taboo. One such subject is masturbation, an activity known but seldom discussed openly, despite being a natural and nearly universal part of the human experience. As individuals seek a deeper understanding of self-care and wellness, it’s important to separate the myths from the facts and recognize the potential health benefits associated with self-love and exploration. In this article, we will shed light on the physical and mental health advantages of masturbation, debunking common misconceptions and addressing frequently asked questions along the journey toward sexual wellbeing and empowerment.
Historic Views on Masturbation
Throughout history, masturbation has been met with varying attitudes and perceptions. In many ancient and pre-modern societies, masturbation was seen as normal and healthy. Greek philosophers like Diogenes and Plato did not condemn masturbation.
During the Middle Ages and in traditional Christian theology, religious leaders took a negative view towards masturbation, seeing it as sinful and immoral. The Catholic Church in particular condemned masturbation as a mortal sin. By the 18th century, some medical experts began arguing that masturbation could cause mental and physical illness. Swiss physician Samuel-Auguste Tissot wrongfully claimed that semen was an essential body fluid, and its loss through masturbation could cause health problems. During the Victorian era, masturbation remained very taboo and was seen as unhealthy.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, attitudes gradually shifted to be more accepting of masturbation. Alfred Kinsey’s research in the 1940s and 1950s found masturbation to be nearly universal behavior. The sexual revolution of the 1960s and 1970s further normalized masturbation. Today, masturbation is generally considered normal, healthy, and not immoral by the medical community. However, some conservative religious groups may still discourage it and this mindset has persisted. In fact, a study has shown that the more religious a person is, the more likely they are to restrict sexual fantasies and masturbation or pleasure in general.
Physical Health Impacts
Regular masturbation has been associated with several benefits related to physical health. For both men and women, sexual activity, including masturbating, helps keep the reproductive system working optimally. Arousal and orgasm can help to circulate oxygen and nutrients through genital tissues and flush waste and bacteria.
For men, masturbating may help prevent benign prostate hyperplasia (enlarged prostate) and prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate) by clearing the prostate of toxins and bacteria. Frequent ejaculation through masturbation may also lower a man’s risk of developing prostate cancer. However, the connection between prostate cancer risk and masturbation is still unclear and requires more research.
For women, masturbating helps circulate nutrients and blood flow to the vagina and vulva, which improves elasticity and lubrication. Regular circulation keeps tissues healthy and functioning well, similar to the benefits of exercise for other parts of the body. Orgasms achieved through masturbation also lead to pelvic contractions that help decrease menstrual cramping and pain. Some studies suggest frequent masturbation may also reduce a woman’s risk of developing yeast infections and urinary tract infections, assuming proper hygiene practices are followed of course.
Overall, regular masturbation seems to provide multiple physical benefits related to sex organ health. However, as with most health topics, more research is needed to fully understand the specific impacts. The available evidence indicates that moderate masturbation as part of a healthy sex life is generally safe and provides physiological benefits.
Mental Health Impacts
The relation between masturbation and mental health is complex and depends on each individual’s circumstances. Masturbation or any other sexual activity, especially when it results in orgasm causes your body to release a number of hormones with varied effects.
- Dopamine: considered one of the “happiness hormones”, triggers your brain’s reward system
- Endorphins: mood boosting and stress relieving, can also give pain relief
- Oxytocin: often called the “cuddle hormone”, promotes social bonding
- Testosterone: improve arousal and stamina
- Prolactin: can boost your mood, immune system, and even improve lactation
All of these hormones can naturally boost your mood and mental state, but the effect is only temporary. You may also have heard of “post nut clarity” where you suddenly feel more focused (and hopefully don’t regret anything you just did). This is believed to be a reaction to the release of the above hormones but this has not been directly studied.
Relation to Sex Life
There is debate over how masturbation impacts people’s actual sex lives.
Some argue that masturbation promotes healthy sexuality by allowing people to explore their desires and gain better understanding of what gives them pleasure. This in turn can lead to better communication of needs with partners and elevated libido.
Others suggest that too much masturbation, especially to unrealistic pornography, may reduce interest and satisfaction in partnered sex. Some believe it can become a compulsive behavior that distracts from sexual intimacy.
However, most experts agree that occasional masturbation done in moderation is unlikely to negatively impact partnered sexuality. The key factors appear to be appropriateness of context and masturbation not becoming the sole outlet for sexual pleasure. Done in a healthy manner, self-stimulation may act as a release, reduce stress, and even energize libido. But relying solely on it without maintaining intimacy and variety in a relationship requires consideration. As with all behaviors, balance and mindfulness are important.
Ethical Considerations
Masturbation, like many behaviors, comes with ethical questions around morality and values. There are differing viewpoints on whether masturbation should be encouraged, discouraged, or considered amoral. Some consider masturbation an immoral act, associated with lust or self-gratification. This viewpoint sees it as contradicting religious or social values around sexuality being limited to procreation or expressions within marriage. However, many today view masturbation as an amoral act, neither inherently good nor bad, but rather a private matter of personal choice. From this perspective, judging or shaming masturbation is seen as unethical.
A separate ethical concern is around appropriateness for children and teens. Views vary on what ages it becomes acceptable, based on maturity and consent factors. Some see exploration as developmentally natural for older children/teens, while others consider it always inappropriate until adulthood. Experts emphasize the importance of education on safe, healthy practices versus feelings of shame.
Overall, ethics around masturbation involve weighing arguments of morality against values of privacy, health, and choice. While some see it as morally questionable, many uphold it as an acceptable and normal private behavior, with appropriate education for developing youth.
Frequency and Addiction
There is limited data on how often people masturbate, for obvious reasons. Most people aren’t exactly going to volunteer how often they’ve done it. Studies have found the frequency varies greatly by age and gender. A recent study suggests that about 1-5 people masturbate at least once a week, with it being more common for men.
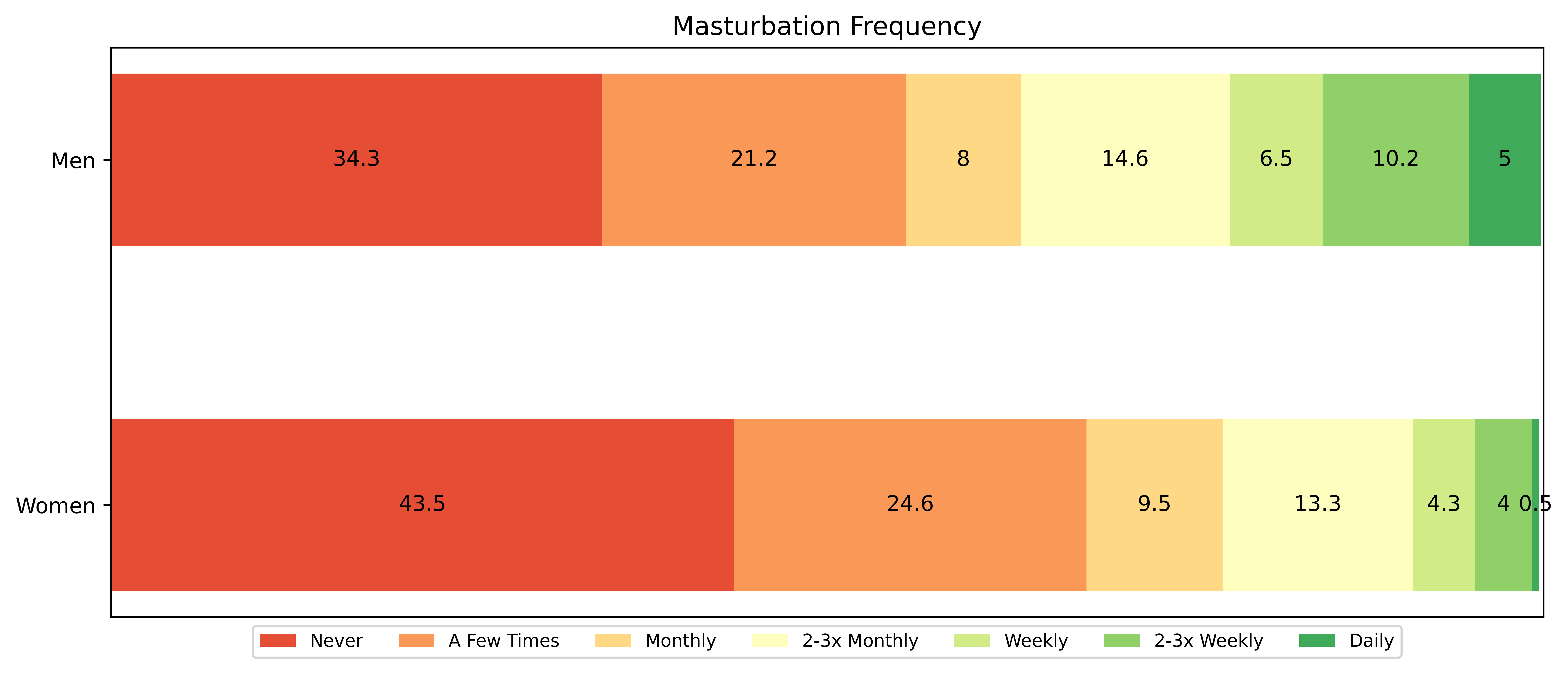
Some individuals worry their masturbation may be excessive or addictive. While a high frequency is not necessarily problematic, masturbation could potentially be compulsive for some. However, mental health experts do not consider masturbation or sex addiction to be clinical diagnoses according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Compulsive sexual behavior is sometimes considered an “impulse control disorder” requiring therapy.
But for most, masturbation is a normal and healthy component of human sexuality, so long as it does not negatively impact relationships, work, or health.
Wrapping Up
The question of whether masturbation is healthy or not depends on many personal and contextual factors. However, based on the evidence reviewed, we can conclude that in general:
- Masturbation in moderation is not likely to cause any significant physical or mental health issues for most people. Excessive masturbation may potentially lead to soreness or relationship problems in some cases.
- Masturbation can help relieve stress and anxiety, and provide pleasure. It is generally considered a normal, healthy sexual behavior when not compulsive or replacing sexual intimacy.
- Cultural and ethical viewpoints on masturbation vary widely. Mutual understanding and open communication with partners is important.
- For those with religious or ethical concerns, masturbation may cause guilt or shame. However, many mental health professionals argue these feelings are cultural rather than inherent harms.
- Some claims around masturbation, such as causing blindness or insanity, have been debunked by modern science and medicine. However, addiction and compulsion are real concerns for a small percentage of the population.
So basically, if you’re feeling a bit wound up, go indulge in some healthy fantasy and get some endorphins. And when you’re done, come back here to the Strawberry Patch and read some more articles or reviews! We can help you learn something new or find your next sex toy.
Catch you on the wild side! 🐺


